Waste recovery
In the latter case, we refer to energy recovery.
Generally speaking, all Kamp Alliance Group projects are part of a ‘Group Environmental Approach’:
From the delivery phase, through project execution, to the demobilisation phase, each member of Kamp Alliance will strive to comply with an ‘HSE’ environmental approach in accordance with the European standards respected by each of the NovaKamp companies.
In this regard, particular attention will be paid to the following aspects, which will comply with the standards in force within the EU
• Waste storage and treatment,
• Use of local resources,
• Reduction of energy consumption,
• Reduction of water consumption,
• Reduction of soil pollution,
• Reduction of air pollution,
• Reduction of noise pollution.
As part of this project, this aspect of the ‘environmental approach’ may be proposed to the client.

Our various Waste recovery solutions

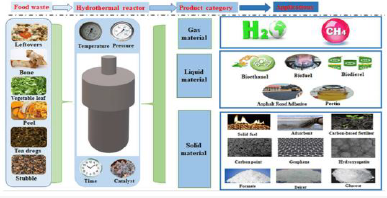
Hydrothermal gasification
Hydrothermal gasification is a type of hydrothermal conversion, or hydrothermal process, which is an industrial process of a physical-chemical nature that involves transforming biomass into combustible materials, particularly biofuels, through hydraulic pyrolysis.
Hydrothermal gasification (aqueous gasification at high temperature and pressure) uses the water contained in biomass in its supercritical state as a reaction medium to produce a methane-rich synthesis gas. The gas produced, under high pressure at the end of the process, can either be injected and stored in the gas network or burned directly to produce heat.
Biomedical waste converts organic matter into combustible gas through reaction with water at high temperature and pressure.
Key advantages:
– Reduction in the ‘base exit’ logistics footprint
– Reduction of risks and costs associated with waste management
– Improved efficiency and safety of facilities
– Significant reduction in the environmental footprint
Recovery:
– Electricity
– Synthetic gas
– Heat
– Hydrogen
– Ash

Incinerator
An incinerator is a device designed to reduce or destroy objects by incineration, i.e. by burning them as completely as possible.
It generally takes the form of a furnace in which the heat released by the materials being burned is sufficient to ignite the materials added.
Capacity: Up to 150 kg/h of waste processed
Key advantages:
– Reduction of the ‘off-site’ logistics footprint
– Customisation options and advanced filtration system
– Energy optimisation for increased performance
– Domestic hot water production & heating
– Easily transportable, simple to use


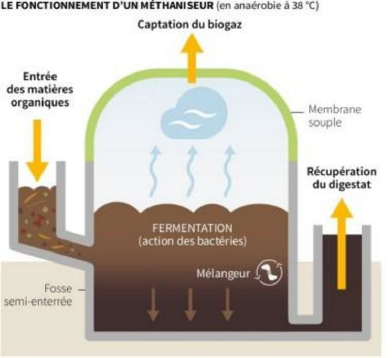
Micro-methanisation
Processes up to 350 kg/day of waste for 100 litres of fertiliser
Key advantages:
– On-site processing reduces CO2 emissions and methane production for each tonne of food waste processed
– Replacement of fossil fuels with clean energy

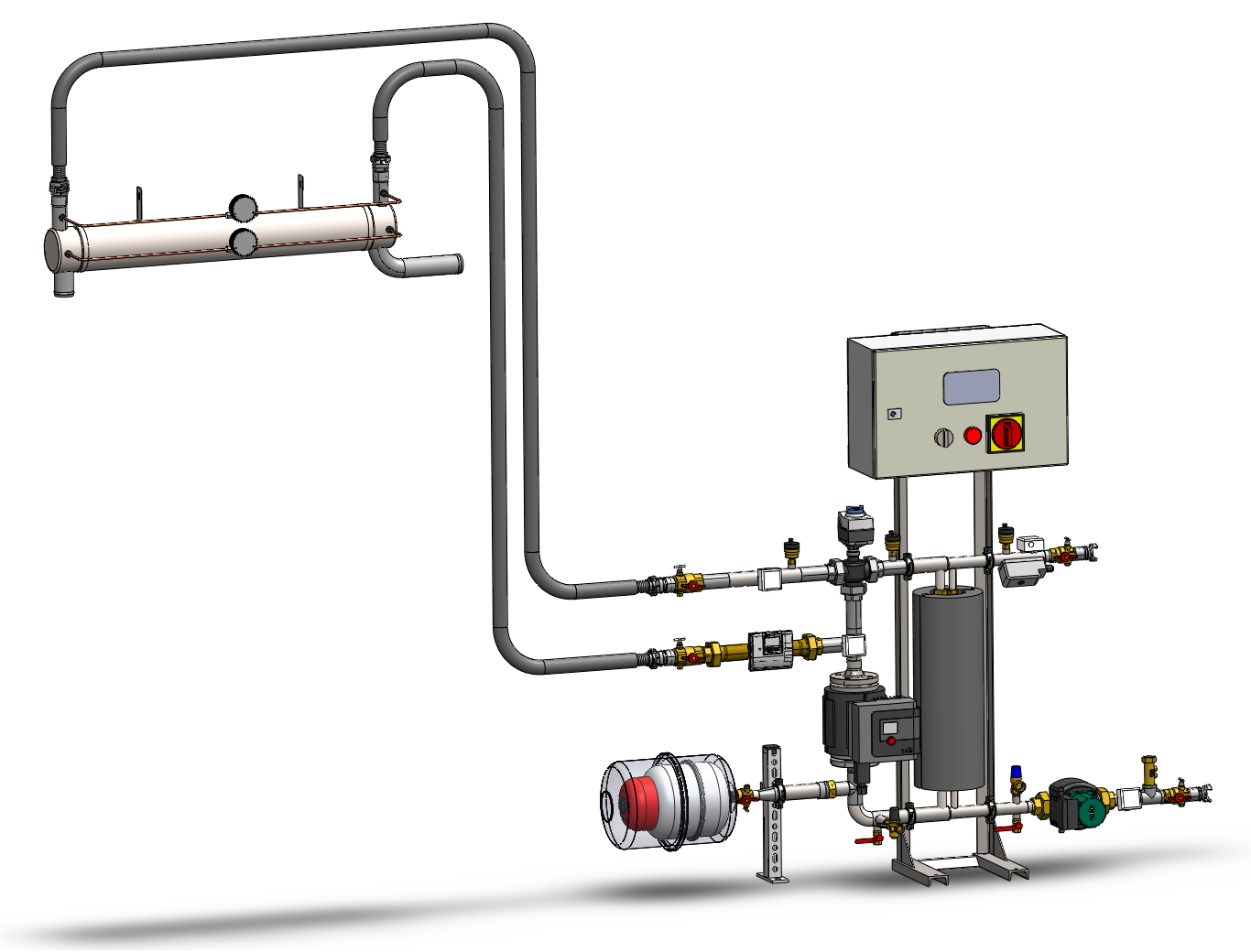
Waste heat recovery
Waste heat, or residual heat, is ‘heat generated by a process that is not its primary purpose and is not recovered’.
Waste heat recovery from the engine cooling system and use for domestic hot water (DHW) production
Recovering waste heat for other uses, in addition to being an industrial opportunity for job creation, is one way to reduce the entropy of a system and thus reduce energy waste by improving its energy efficiency.

Plastic pyrolysis
Plastic pyrolysis is a distillation process that converts plastic waste into fuel.
The waste is heated to over 400°C in a first tank and converted into gas. Depending on the condensation
(cooling) temperatures of this gas, different types of fuel are obtained.
Requires plastic sorting.

Wastewater treatment and reuse
Wastewater treatment refers to all processes aimed at purifying wastewater before it is returned to the natural environment or reused. Wastewater is water that, following domestic, commercial or industrial use, is likely to pollute the environment into which it would be discharged.
For this reason, in order to protect receiving environments, treatment is carried out on these effluents collected by the urban or private sewerage network. The aim of treatment is to minimise the impact of wastewater on the environment.
When treated water is reused, this is referred to as wastewater recycling.
With many years of experience, Kamp Alliance has developed deployable wastewater treatment units that can be set up in just a few days – excluding infrastructure.

Our othersolutions

Water cycle

Multi-technical solutions

Design offices and field experts
